- Home
- About Us
- Workflow
- Projects
- Customer Feedback
- Private Policy

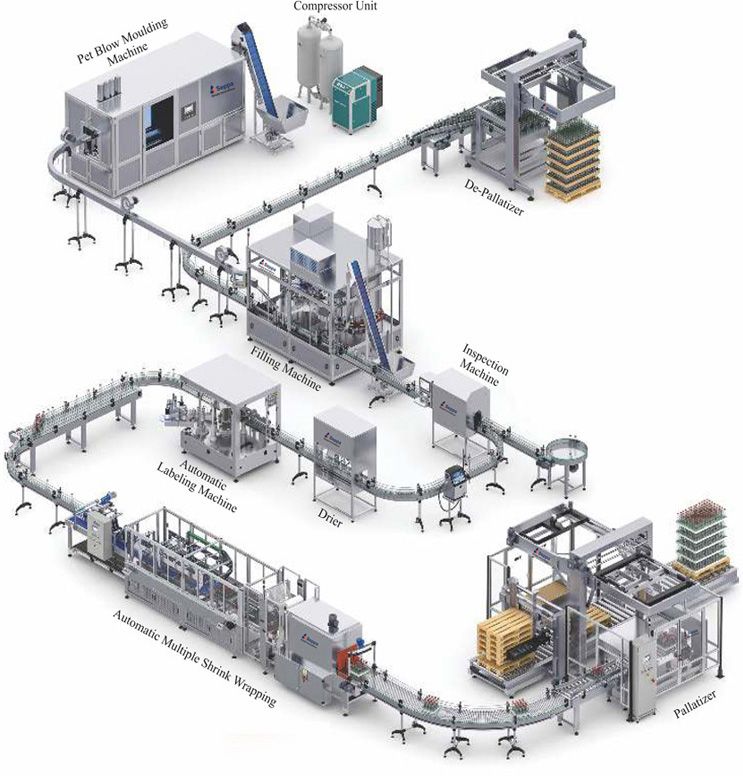
- Products
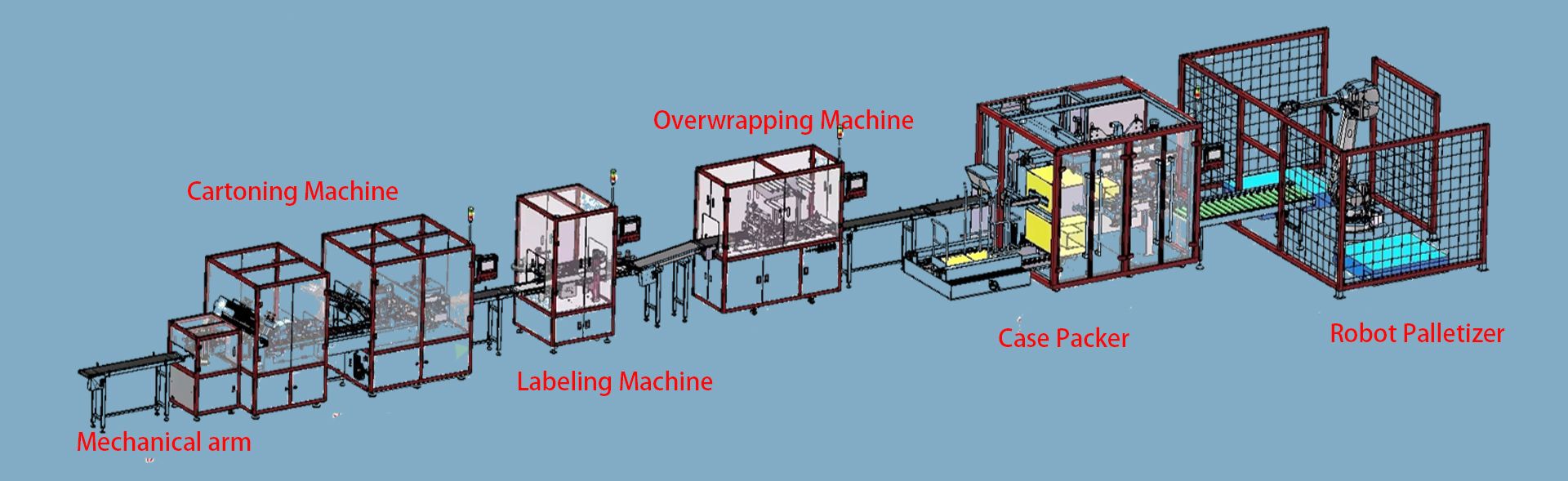
- Overwrapping Machine
- Cartoning Machine
- Case Packer
- Labeling Machine
- Shrink Wrapping Machine
- Case Erector
- Case Sealer
- Check Weigher
- Strapping Machine
- All-side Ironing Machine
- Tea Bag Packing Machine
- Packaging Materials
- Pillow Type Packing Machine
- Filling And Capping Machine
- Tube Sealing Machine
- Solutions
The key points in the basic operation process of automated warehouse2021-03-16The key points in the basic operation process of automated warehouse
Automated three-dimensional warehouses are widely used in tobacco, machinery, electronics, chemicals, textiles, printing and publishing, pharmaceuticals, food, ports, airports, commercial distribution, transportation and other industries. They are important storage facilities for enterprises.
The operation of automated three-dimensional warehouses has a significant effect on improving the logistics efficiency of enterprises. However, many people are very curious, what is the difference between the basic operation process of automated warehouse and ordinary warehouse?
What are the key points worthy of our attention in each process? In this article, I will use the simplest and clearest text to understand with you:
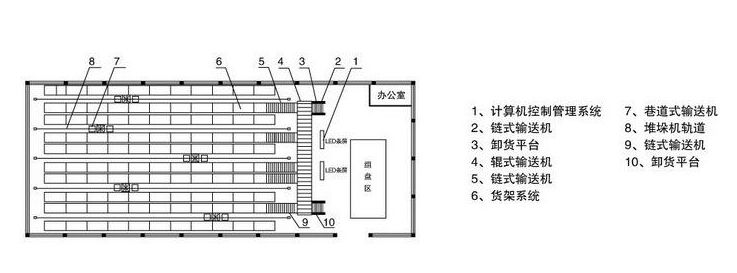
The main body of the automated three-dimensional warehouse is composed of racks, laneway stacking cranes, entry (exit) warehouse workbenches, and automatic transport (exit) and operation control systems.
The shelf is a building or structure with a steel structure or a reinforced concrete structure. The shelf is a standard size cargo space. The lane stacking crane runs through the lane between the shelves.
Complete the work of storing and retrieving goods; use the WCS system to control the management. The following is the basic operation process of automated warehouse:

Warehousing process: The system responds to the warehousing request and pops up the warehousing dialog box, and the user fills in the name and quantity of the goods in the warehouse;
The system queries the order quantity. If the order quantity is greater than the inventory quantity of the goods, an alarm will be given. Otherwise, the system will send a warehousing operation task list to the warehousing computer, and print the warehousing receipt, and the warehousing computer controls the barcode system to scan the goods;
After scanning, the warehousing computer will judge whether the scanned goods are consistent with the task. If they match, the warehousing sorting and transportation will be performed. If they do not match, an alarm signal will be given.

02
Assembling and binning: Before the small-size goods or parts are put into the warehouse, it is generally necessary to perform the assembling and binning operation to meet the storage requirements and make full use of the cargo space. Large-size goods can be directly put into the warehouse or put into the pallet according to the situation Warehousing.
Generally, a fixed assemblage and box method is adopted, that is, multiple goods or parts of the same kind are placed in a pallet or box.
In some cases, in order to further increase the storage capacity, it is possible to adopt the mode of assembling and boxing of loose parts, that is, assembling into boxes of random varieties and numbers. In this mode,
It is necessary to set the information such as the batch code of the assortment, the batch code of the assortment, the batch code of the goods and parts in the database of the management system, and link the quantity and type of the goods in each assortment with its storage location, so as to facilitate the dumping when leaving the warehouse LCL.

Barcode scanning input: The barcode that characterizes the goods generally contains four kinds of information: pallet number, goods number, batch number and quantity. The barcode is read in by the scanner, decoded by the decoder, and then transferred to the computer via the serial port interface.

Outbound process: The outbound process of goods is as follows: the system responds to the outbound request, and the outbound dialog box pops up, and the user fills in the name and quantity of the outbound goods;
The system inquires about the inventory, and if the outbound quantity is greater than the inventory quantity of the goods, an alarm will be given; otherwise, the system will send an outbound operation task list to the outbound computer and print out the warehouse receipt.
The outbound computer issues an outbound instruction to the stacker, and the stacker ships from the shelf, and may be transported to the outbound station, and the outbound computer controls the barcode system to scan the goods;
After scanning, the outbound computer will determine whether the scanned goods are consistent with the task. If they match, they will perform outbound sorting and sub-packaging. If they do not match, an alarm signal will be given.
About us- Tel: +86-510- 85868879
- E-mail: sales@siciauto.com
- Address: No.132-4, Rongyu Road, Xishan Economic Development Zone, Wuxi City, Jiangsu Province, China.
- SUPPLIER







- PROJECTS







Wuxi Sici Auto Co., Ltd. Boxmedia







